Overview
In this lecture, we discuss processor cache performance and transition to the process control unit.
Full lecture notes on process control — Textbook readings
Processor cache
- Processor caches divide primary memory into blocks of ~64 aligned bytes
- 128 bytes on some machines
- C++ has a name or the block size:
std::hardware_constructive_interference_size(andstd::hardware_destructive_interference_size)
- Processor implements prefetching strategies
- Sequential access often beneficial
- User can help:
prefetchinstruction
Machine learning Matrix multiplication
- Matrix is 2D array of numbers
- m\times n matrix M has
m rows and n columns
- M_{ij} is the value in row i and column j
- How to store a 2D matrix in “1D” memory?
- Row-major order
- Store row values contiguously in memory
- Single-array representation
MxNmatrix stored in arraym[N*M]- Matrix element M_{ij} stored in array element
m[N*i + j] - 4x4 matrix: A_{0,0} :=
a[0]; A_{0,1} :=a[1]; A_{0,2} :=a[2]; …; A_{3,2} :=a[14]; A_{3,3} :=a[15]
Matrix multiplication definition
- Product of two matrices C = A \times B
- If A is m\times n, then B must have dimensions n\times p (same number of rows as A has columns), and C has dimensions m \times p
- C_{ij} = \sum_{0\leq k < n} A_{ik}B_{kj}
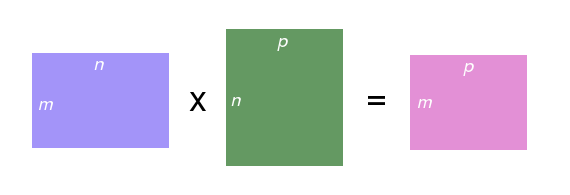
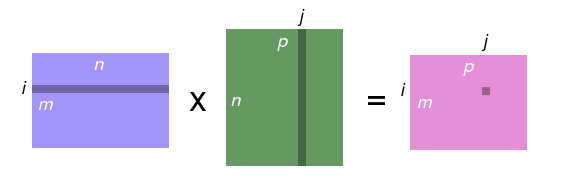
Implementing matrix multiplication
// clear `c`
for (size_t i = 0; i != c.size(); ++i) {
for (size_t j = 0; j != c.size(); ++j) {
c.at(i, j) = 0;
}
}
// compute product and update `c`
for (size_t i = 0; i != c.size(); ++i) {
for (size_t j = 0; j != c.size(); ++j) {
for (size_t k = 0; k != c.size(); ++k) {
c.at(i, j) += a.at(i, k) * b.at(k, j);
}
}
}
Question
- Can you speed up
matrixmultiply.ccby around 10x?
Processes
- A process is a program in execution
- Processes isolation makes processes modular
- They behave mostly independently
- An error in one process won’t crash system
- A performance problem in one process may not affect others
Process coordination
- Modularity makes systems more reliable and capable
- Improvements to one component can improve the overall system
- New combinations of components can implement new functions
- Wheels + gear + pedal = bicycle—a whole greater than the sum of its parts
- Let’s use multiple processes to accomplish complex tasks!
- Turn processes into components
- Take advantage of available resources: when one process is paused (e.g., accessing storage), run another
- What tasks are involved in coordinating processes?
- Starting new processes
- Terminating running processes
- Monitoring processes for completion
- Communicating among processes
- The prototypical program that coordinates other processes: the shell
Basic shell operation
- Print a prompt
- Wait for user to enter a command line
- Execute the command line in a new process or processes
- Wait for the command line processes to complete
- Repeat
Simple shell commands
$ echo foo
foo
$ sleep 5
$is the prompt (yours are longer)echo fooandsleep 5are simple command linessleep 5behavior shows that the shell waits for a command to complete
Process control system calls
- What sub-tasks are required for process coordination?
- Create a process:
fork - Run a different program:
execfamily - Terminate a process:
_exit - Monitor completion:
waitpid
Process = image + identity + environment view
- Image: contents of primary memory and registers
- Code, data, stack, and heap
- Command line arguments (
argc,argv) - Directly managed by process
- Identity: process names
- Process ID
- Process relationships (parent process ID)
- Ownership, timing, etc.
- Managed by kernel; process influence constrained by policy
- Environment view: connections among processes and devices
- Open file descriptors, file positions
- Lives in kernel, managed by process using system calls
- Each process has its own view of the environment, but the underlying storage is shared
fork creates a new process
pid_t fork()pid_t=int
- Return value:
- 0, to the new process
- Process ID (pid) of new process, to the original process
- New process has:
- Cloned image
- New identity
- Cloned environment view
fork, stdio, and coherence
storage/fork1.cc./fork1vs../fork1 | cat
storage/fork2.cc./fork2vs../fork2 | cat
Process hierarchy
- Every process has a parent process
getpidsystem call: Return current process IDgetppidsystem call: Return parent process IDforkcreates a new child process
- Root of process hierarchy is process with ID 1 (
init)- What happens if a parent process dies before its child?
fork: Which runs first?
The uniq utility
uniqsearches for consecutive duplicate linesExample 1 Example 2 Example 2 Example 3 Example 2uniq: Print only one of each set of duplicatesuniq -c: Precede each line with a count of duplicatesuniq -u: Only print non-repeated linesuniq -d: Only print repeated lines
minishell.cc
Question
- What are the most complete assertions you can come up with that relate the
p*variables? Assumeforkdoes not fail.
pid_t p1 = getpid();
pid_t p2 = getppid();
pid_t p3 = fork();
pid_t p4 = getpid();
pid_t p5 = getppid();
assert(???);
Some answers
assert(p1 > 0 && p2 > 0 && p4 > 0 && p5 > 0): all process PIDs are >0assert(p3 >= 0):forkdid not fail (it’s >0 in parent, 0 in child)assert(p1 != p2 && p4 != p5): a process’s PID ≠ its PPIDassert(p4 != p2): new PID ≠ original PPIDassert(p1 != p3 && p2 != p3): child PID ≠ parent or grandparent PIDassert(p3 != 0 ? p1 == p4 : p1 == p5)- In parent (
p3 != 0), original PID == new PID - In child (
p3 == 0), original PID == new PPID
- In parent (
assert(p3 != 0 ? p2 == p5 : p2 != p5)- In parent (
p3 != 0), original PPID == new PPID - In child (
p3 == 0), original PPID ≠ new PPID
- In parent (